Welcome to the deep dive on ASML, conducted together with my colleague Akim (Etcaetera).
In this comprehensive analysis, we will explore various facets of this leading technology company. In part one, I will discuss the investment thesis and provide a comprehensive business overview. Then, in part two, Akim will delve into the stock performance, the hard figures (financials and valuation) and outline the risk factors. Make sure to follow Etcaetera for part two of this analysis.
Investment Thesis
ASML has an incredible moat (competitive advantage) that makes it a monopoly in the strategic semiconductor chips chain. Chips power everything: from your phone, to your laptop, to your car. Chips are absolutely essential to the AI transition that is unfolding. As AI continues to expand, so will ASML's growth. Let’s first dive into the technological leadership the company has.
Leadership in Lithography Technology
ASML stands at the forefront of lithography technology, being the leading supplier of advanced lithography equipment, including Deep Ultraviolet (DUV) and Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) systems. These cutting-edge technologies are essential for producing the high-performance chips necessary for AI applications. ASML’s unique capability in EUV lithography provides it with a monopolistic edge, supplying the indispensable tools for cutting-edge semiconductor manufacturing, which directly impacts AI chip production.
Growing AI Market Demand
The rapid adoption of AI across various sectors is fueling an unprecedented need for more powerful and efficient semiconductor chips. AI applications demand increasingly sophisticated and smaller transistors, which only ASML’s advanced lithography machines can produce. As AI technologies proliferate in industries such as healthcare, automotive, finance, and consumer electronics, the demand for chips optimized for AI tasks will continue to grow, consequently benefiting ASML’s business.
"Current generative AI and other technologies have the potential to automate work activities that absorb 60 to 70 percent of employees' time today. Half of today's work activities could be automated between 2030 and 2060, with a midpoint in 2045." - McKinsey and Company
Generative AI could add $2.6 - $4.4 Trillion annually to the global economy
Strategic Position in the Semiconductor Ecosystem
ASML’s equipment is indispensable to the world’s leading semiconductor manufacturers, including TSMC, Samsung, and Intel, who are pivotal suppliers of AI chips. As these companies scale their AI chip production to meet market needs, their reliance on ASML’s lithography systems will intensify. Continuous investments by semiconductor companies in AI capabilities ensure sustained long-term demand for ASML’s advanced lithography machines.
Secular Growth Driven By Digital Transformation
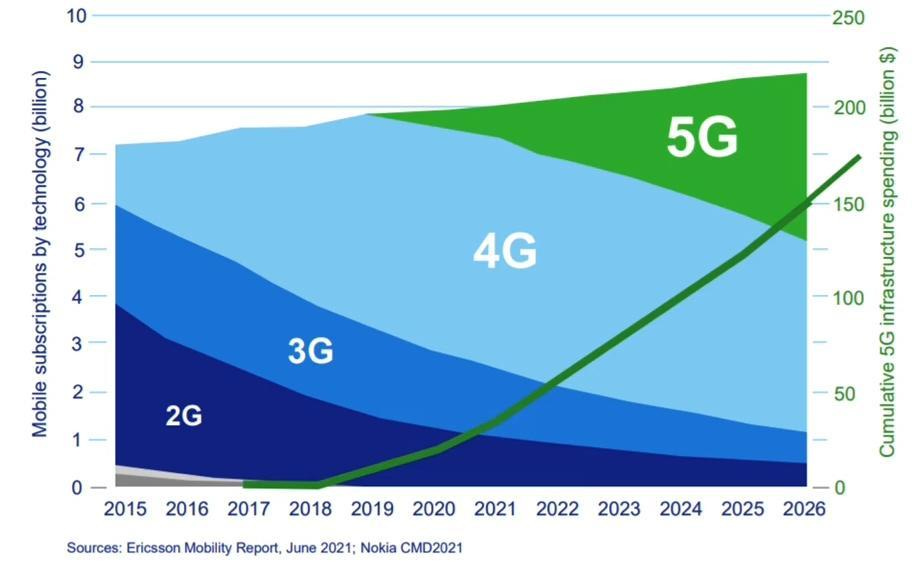
The shift from 4G to 5G is driving a significant increase in the demand for semiconductor chips, both in terms of quantity and precision. Currently, there are an estimated 40 billion connected devices globally, which translates to about 5 devices per person. This number is projected to grow to 350 billion by 2030, or approximately 41 devices per person. ASML stands to benefit from this surge in demand for both less precise, mass-market chips and the cutting-edge, leading-edge chips.
When The Ecosystem Grows, ASML Grows
ASML operates within an industry where its customers are some of the largest companies in the world. These customers rely heavily on ASML’s lithographic systems to manufacture their chips. As these companies expand, the demand for ASML's equipment will continue to rise.
In 2020, the top 50 technology companies within the ecosystem generated $493 billion in EBIT. This figure has been growing at an annual rate of more than 10% since 2016, illustrating the robust growth and increasing profitability within this sector.
Business overview
ASML Holding N.V. (ASML) is a leading company that makes specialized machines for companies that produce computer chips. These chips are essential for everyday devices like smartphones, tablets, computers, and medical equipment. ASML is especially known for its advanced technology, including being the only company that makes a crucial type of machine called Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography systems.
Instead of making all the parts themselves, ASML works with around 500 suppliers to assemble these complex machines. This approach helps them keep up with the latest technology, ensuring that the products we use every day are powered by the most advanced chips.
Photo-lithography System
ASML's photo-lithography system works like a light projector. It shines light through a pattern, which is then shrunk and focused onto silicon wafers that are sensitive to light. This process creates the tiny chips used in many everyday products, from smartphones and laptops to medical devices and household appliances.
ASML sells these machines, which help chip manufacturers make the microchips essential for these devices. They offer different types of systems, including Deep Ultraviolet (DUV) and Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV), each playing a key role in improving chip performance and enabling new innovations in technology.
Deep Ultraviolet (DUV) System
DUV systems are designed to be highly efficient, capable of processing up to 300 wafers per hour. These wafers are used to make advanced chips for things like phone processors and computer servers. DUV machines are expensive, costing between $10 million and $70 million, not including maintenance and parts. ASML also earns ongoing revenue from maintaining and replacing parts for these machines.
Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography
EUV systems are the most advanced and expensive machines ASML offers. They are specifically designed to help clients make the most cutting-edge chips. Major tech companies like TSMC, Apple, Samsung, SK Hynix, Micron, and Intel use EUV technology in their chip manufacturing processes. Each EUV machine costs between $150 million and $318.6 million, reflecting their complexity and importance in advancing chip technology.
Mass Metrology & Inspection
Mass Metrology involves checking the weight and quality of wafers after they've gone through different processes in chip manufacturing. ASML’s YieldStar systems are essential for ensuring the patterns on these wafers are accurate at every stage. The YieldStar 1375F and 1385 models are unique because they are the only tools that can measure multiple layers of the print pattern at once.
Revenue Sources
ASML’s revenue is primarily derived from two main sources: system sales, which make up approximately 72% of their revenue, and service and field option sales, contributing around 28%. It essentially makes money from selling new machines and from the maintenance and repairs of these machines.
Regarding lithography systems, the number of units (excluding metrology and inspection systems) has increased from 79 to 90 year-to-date (YTD). Net bookings for lithography systems (excluding High-NA EUV systems) have grown from 178 to 200 units YTD.
Revenue distribution by geographical location is currently as follows:
Taiwan: 32%
South Korea: 29%
China: 18%
U.S.: 13%
Japan: 5%
EMEA: 3%
Others: 0.5%
Thank you for reading, and stay tuned for part two, where Etcaetera will dive into the risks involved and the company's valuation to determine if ASML is a worthy buy.
Timothy & Akim.
Connect with me on:
🟦 Linkedin: Timothy Assi
🟪 Instagram: @panic_drop
⬛ X: @timoassi













Hi - Do you have any analysis on Arm holdings
It was an absolute pleasure analysing ASML with you! Part II is coming tomorrow. I bought more shares today though! 😄